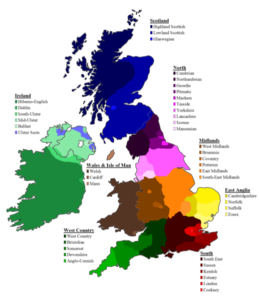
The United Kingdom is known for its rich linguistic tapestry, with a diverse range of accents and dialects that reflect its historical, cultural, and regional variations. From the rolling hills of Scotland to the bustling streets of London, each region has its own distinct accent, often revealing the fascinating origins and influences behind them.
Received Pronunciation (RP):
Also known as «BBC English» or «Queen’s English,» RP is often associated with the upper class and is considered a standard accent for broadcasting. Its origins can be traced back to the speech patterns of the British elite in the 18th century. However, it is worth noting that RP is less common in everyday conversations and has been gradually evolving over time.
Cockney:
The Cockney accent is closely associated with the working-class communities of East London. It is characterized by its distinctive vowel sounds and rhyming slang. Cockney accents are believed to have emerged in the 19th century among the working-class population in the East End of London.
Geordie:
The Geordie accent hails from the Newcastle and Tyneside region in northeast England. It is known for its unique pronunciation, with elongated vowel sounds and the distinctive «oo» sound. Geordie is deeply rooted in the local dialect of the area and has its origins in the speech of the coal miners and shipyard workers.
Scouse:
The Scouse accent is closely associated with the city of Liverpool and its surrounding areas. It gained prominence in the 19th century due to Liverpool’s role as a major port city. The accent is characterized by a distinctive sing-song quality and features such as the softening of «t» sounds.
Welsh English:
In Wales, English is spoken with a distinct Welsh accent. Welsh English retains many features of the Welsh language, such as the «ll» sound and the pronunciation of certain vowels. The Welsh accent varies across different regions of Wales, reflecting the linguistic diversity within the country.
Scottish accents:
Scotland boasts a range of distinct accents, including the Glaswegian accent from Glasgow, the Edinburgh accent, and the Highland accent. Scottish accents often have a strong, rolling «r» sound and distinct vowel pronunciations. The accents have evolved over centuries and are influenced by Gaelic, Norse, and other historical factors.
Irish accents:
While Ireland is not part of the United Kingdom, it is worth mentioning the Irish accents due to their cultural significance. Irish accents encompass various regional dialects, including the Dublin accent, the Cork accent, and the Northern Irish accent. These accents reflect the complex history and linguistic diversity of the island.
The United Kingdom’s accents provide a glimpse into the country’s diverse linguistic heritage and regional identities. From the prestigious RP to the vibrant dialects of Cockney and Geordie, each accent tells a story of historical, social, and cultural influences. Embracing these accents and their origins adds depth and richness to the linguistic tapestry of the United Kingdom.
Glossary:
Elongated – Alargado
Norse – Nórdico antiguo
Port city – Ciudad portuaria
Rhyming slang – Jerga rimada
Sing-song – Melódico
Softening – Suavización
Vowel – Vocal
Working-class – Clase trabajadora
